CCNA1 Gene Cloning, Tissue Expression and Its Polymorphic Association with Egg Production Traits in Ducks
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.4238/3pkx3q56Keywords:
CCNA1 gene, gene cloning, polymorphism, egg production traits, association analysisAbstract
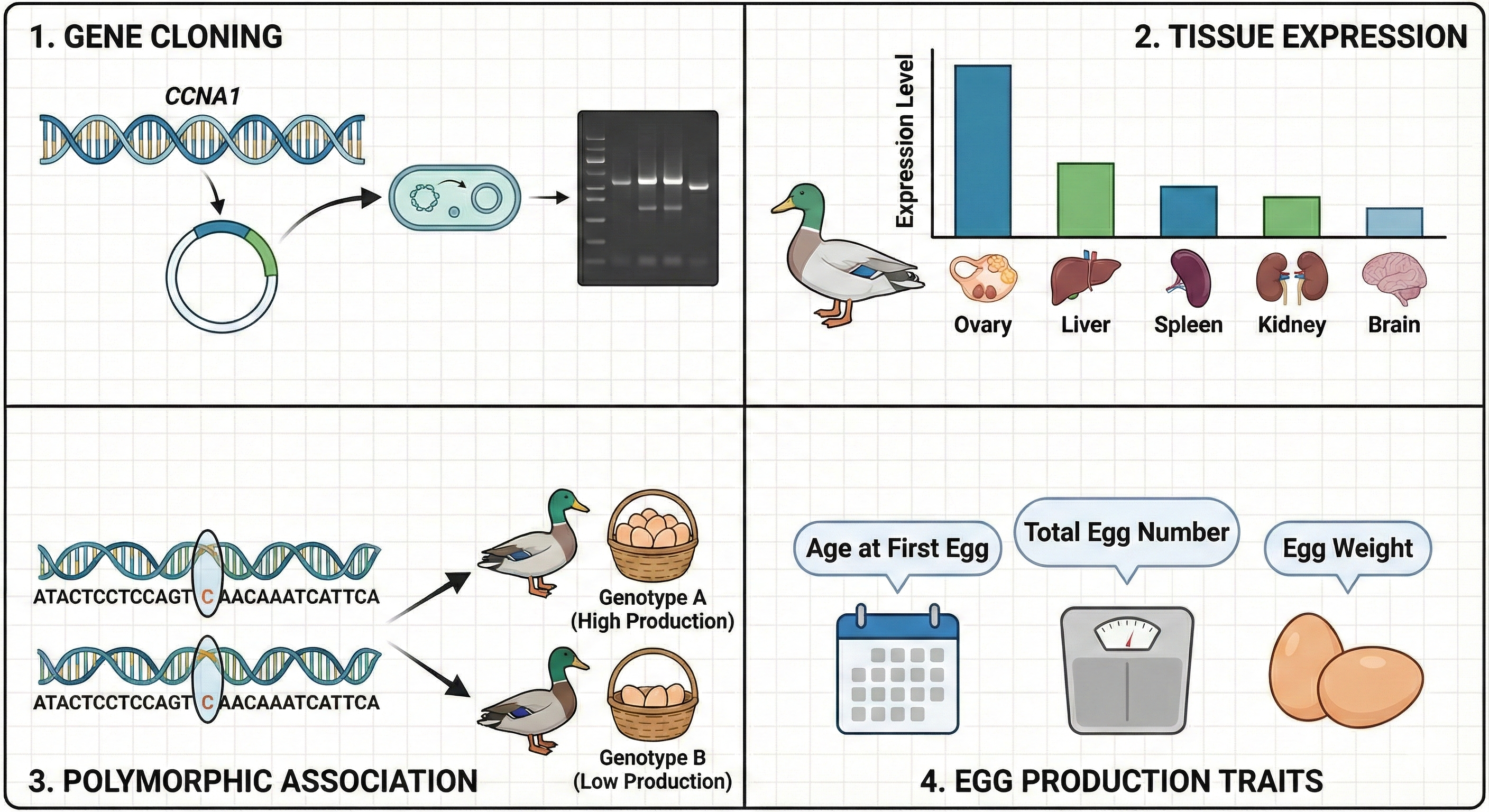
To explore the polymorphisms of CCNA1 gene and their association with the egg production traits in ducks, the real-time PCR (RT-PCR) was used to detect the CCNA1 gene expression differences in different tissues and identify SNP sites by the DNAStar software MegAlign program combined with the sequencing peak map, to find the association of egg production traits with the polymorphic locus and haplotype combinations. The results showed that the mRNA expression level of the CCNA1 gene was the highest in the ovarian tissue. Six SNP sites, including g.1223 A>G,g.1600 T>C,g.1874 T>C,g.1901 C>T,g.1926 T>C and g.1931 G>A affected the egg production traits in ducks were detected. Association analysis showed that individuals with haplotype H3H4 had the highest DDP, while H2H2 individuals exhibited the highest AEW. The results suggested that the CCNA1 gene may be used as a candidate molecular marker to improve egg production traits in ducks. This study provides a scientific basis for further exploring the role and molecular mechanism of CCNA1 in the reproductive performance of ducks.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Yifu Rao, Ai Liu, Wei Li, Jiaoyi Yang, Fuyou Liao, Binnong Yao, Shenglin Yang, Boonanuntan Surintorn (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.



